Alcohol ethoxylates (AEs) are one of the most widely used non-ionic surfactants across agriculture, personal care, industrial cleaning, and specialty chemical formulations. Known for their excellent wetting, emulsifying, and dispersing properties, alcohol ethoxylates play a critical role in improving formulation efficiency, compatibility, and performance.
Produced by reacting fatty alcohols with ethylene oxide, alcohol ethoxylates offer a unique balance of hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics. This structure allows them to function effectively in complex formulations where stability, uniform distribution, and controlled interaction with active ingredients are essential.
From crop protection and fertilizers to cosmetics, polymer emulsions, and pharmaceutical excipients, alcohol ethoxylates are valued for their versatility, cost efficiency, and non-ionic nature. This guide explores what alcohol ethoxylates are, how they work, their structure, key applications, chemical grades, and important safety considerations.
What Is Alcohol Ethoxylate?
Alcohol ethoxylates are non-ionic surfactants formed by the ethoxylation of fatty alcohols using ethylene oxide. They belong to the broader category of ethoxylated surfactants and are widely used as wetting agents, emulsifiers, detergents, and dispersants.
Because they carry no electrical charge, alcohol ethoxylates demonstrate high compatibility with a wide range of formulation ingredients, including acids, bases, salts, pesticides, and polymers. This makes them especially suitable for multi-component systems used in agriculture, cosmetics, and industrial applications.
Depending on the degree of ethoxylation, alcohol ethoxylates can be tailored for specific performance needs such as improved solubility, enhanced emulsification, or controlled foaming behavior.
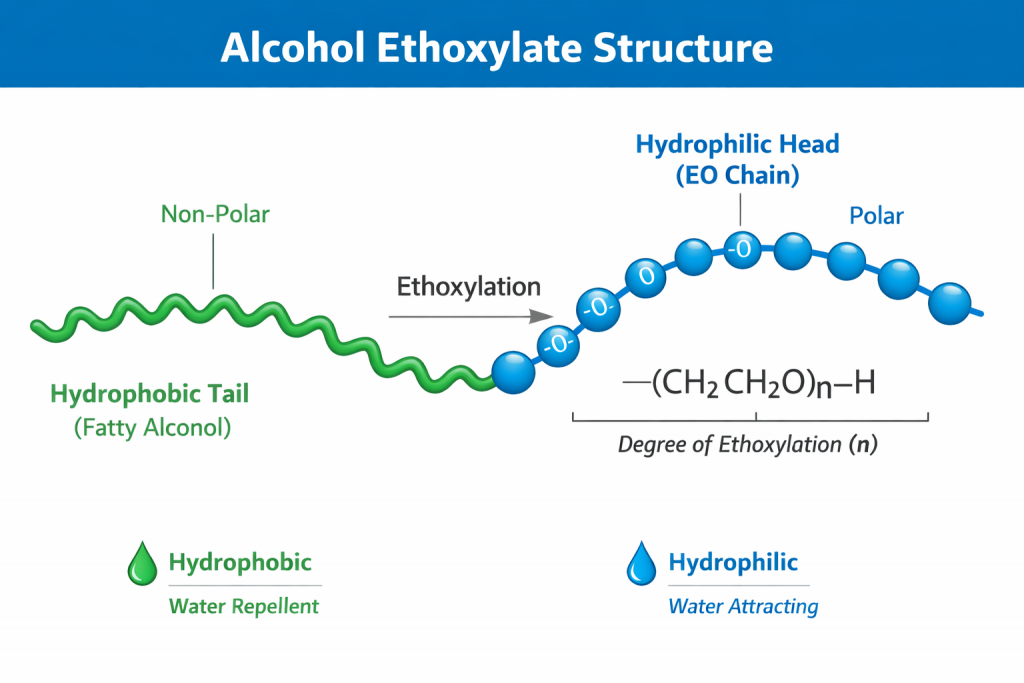
Alcohol Ethoxylate Structure
The structure of an alcohol ethoxylate consists of two main components:
Hydrophobic tail: Derived from fatty alcohols (linear or branched), responsible for interacting with oils, waxes, and hydrophobic surfaces
Hydrophilic head: A chain of ethylene oxide (EO) units that attracts water and provides solubility
The number of EO units—often referred to as the degree of ethoxylation—directly influences the surfactant’s properties, including cloud point, solubility, emulsifying strength, and detergency.
This dual structure enables alcohol ethoxylates to reduce surface tension, stabilize emulsions, and improve the dispersion of active ingredients in both aqueous and non-aqueous systems.
Types of Alcohol Ethoxylates
Alcohol ethoxylates are available in several forms, depending on the alcohol source and molecular structure:
1. Linear Alcohol Ethoxylates
Linear Alcohol Ethoxylates from linear fatty alcohols offer excellent biodegradability and are widely used in agriculture, detergents, and industrial cleaning applications.
2. Branched Alcohol Ethoxylates
Produced from branched alcohols, they provide enhanced stability and performance in high-temperature or chemically demanding environments.
3. Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates
Commonly used in personal care and cosmetic formulations due to their mildness and effective emulsifying properties.
4. Alcohol Alkoxylates
A broader category that includes ethoxylates and propoxylates, offering additional formulation flexibility for specialized industrial uses.
Applications of Alcohol Ethoxylates
Alcohol ethoxylates are used across multiple industries due to their adaptability and performance:
Agriculture: Wetting agents, spreaders, and emulsifiers in fertilizers, herbicides, insecticides, and foliar sprays
Personal Care & Cosmetics: Emulsifier in cosmetics, cleansing agents, and solubilizers
Industrial Cleaning: Detergents, degreasers, and surface cleaners
Polymer & Chemical Processing: Stabilization of polymeric emulsions and dispersions
Pharmaceuticals: Used as formulation aids and excipients to enhance solubility and stability
Their non-ionic nature ensures consistent performance even in hard water and complex tank-mix systems.
Alcohol Ethoxylates in Cosmetics & Personal Care
In cosmetic and personal care formulations, alcohol ethoxylates function primarily as emulsifiers, solubilizers, and cleansing agents. They help blend oil and water phases, improve texture, and enhance product stability.
Fatty alcohol ethoxylates and related surfactants such as ethoxylated castor oil are commonly used in creams, lotions, shampoos, and cleansers due to their mildness and formulation flexibility.
Their ability to maintain stable emulsions while being compatible with a wide range of active ingredients makes them a preferred choice in modern cosmetic chemistry.
Chemical Grades of Alcohol Ethoxylates
Alcohol ethoxylates are manufactured in different chemical grades based on application requirements:
Industrial Grade: Used in detergents, cleaning agents, and industrial emulsions
Agricultural Grade: Designed for compatibility with fertilizers, pesticides, and crop protection formulations
Cosmetic / Pharmaceutical Grade: Higher purity standards for personal care and excipient use
Selecting the appropriate grade ensures regulatory compliance, formulation stability, and optimal performance.
Alcohol Ethoxylate Dangers & Safety Considerations
Alcohol ethoxylates are generally considered safe when used correctly. However, safety concerns may arise from improper handling, overuse, or confusion with alkylphenol ethoxylates (APEOs), which have stricter environmental restrictions.
Key safety considerations include:
Proper dosage and formulation control
Avoiding confusion between APEOs and alcohol ethoxylates
Compliance with environmental and regulatory guidelines
When responsibly formulated, alcohol ethoxylates offer an effective and environmentally acceptable surfactant solution.
Why Choosing the Right Fertilizer Is Crucial
Fertilizers directly influence crop quality, yield, and long-term soil sustainability. When used alongside surfactants such as linear alcohol ethoxylate, ethoxylated surfactants, or ethoxylated fatty alcohols, nutrient uptake becomes more effective and uniform.
Plants require balanced macronutrients (N, P, K) and essential micronutrients (Iron, Zinc, Manganese, Copper, Boron, Chlorine, etc.). The wrong fertilizer or incompatible formulation components can lead to nutrient lockout, reduced productivity, or even soil degradation. Alcohol ethoxylates help improve spreading, penetration, and distribution of fertilizers, especially in liquid and foliar applications.
How Alcohol Ethoxylates Fit Into This Process
- Enhance wetting and spreading of fertilizer solutions
- Improve penetration of nutrients into the leaf cuticle
- Stabilize emulsions in EC, EW, ME, SC, and OD formulations
- Increase uniformity and efficiency of crop inputs
- Reduce wastage through better delivery
Although generally considered safe, it is still important to understand alcohol ethoxylate dangers related to misuse, over-concentration, or environmental persistence. Proper dosage and adherence to recommended application guidelines eliminate most risks.
Conclusion
Alcohol ethoxylates continue to play a vital role across modern chemical formulations due to their versatility, performance, and compatibility. Whether used in agriculture, personal care, industrial cleaning, polymer emulsions, or pharmaceutical applications, their non-ionic nature and tunable structure make them a reliable choice for formulators seeking consistency and efficiency.
Understanding the structure, types, applications, and safety considerations of alcohol ethoxylates allows manufacturers and formulators to make informed, performance-driven decisions. Selecting the right grade and formulation approach not only improves end-product efficiency but also supports regulatory compliance and long-term sustainability.
At SBR International, we specialize in supplying high-quality alcohol ethoxylates and ethoxylated surfactants tailored to the needs of agriculture, personal care, and industrial formulations. With a strong focus on product consistency, technical support, and global sourcing expertise, SBR International partners with formulators to deliver reliable solutions for complex chemical applications.
As formulation requirements continue to evolve, working with an experienced specialty chemical distributor ensures access to the right materials, technical insight, and dependable supply chains—helping businesses innovate with confidence and precision.
Frequently Asked Questions